Data Contracts for Power Users
This section provides a detailed, technical overview of the analytics model for data analysts and other power users. It covers data consistency, table structures, and performance patterns.
For a high-level introduction and ready-to-use queries, please see the Start Here guide and the Cookbook.
Overview & Onboarding
What’s in the box
The analytics model covers the following business domains:
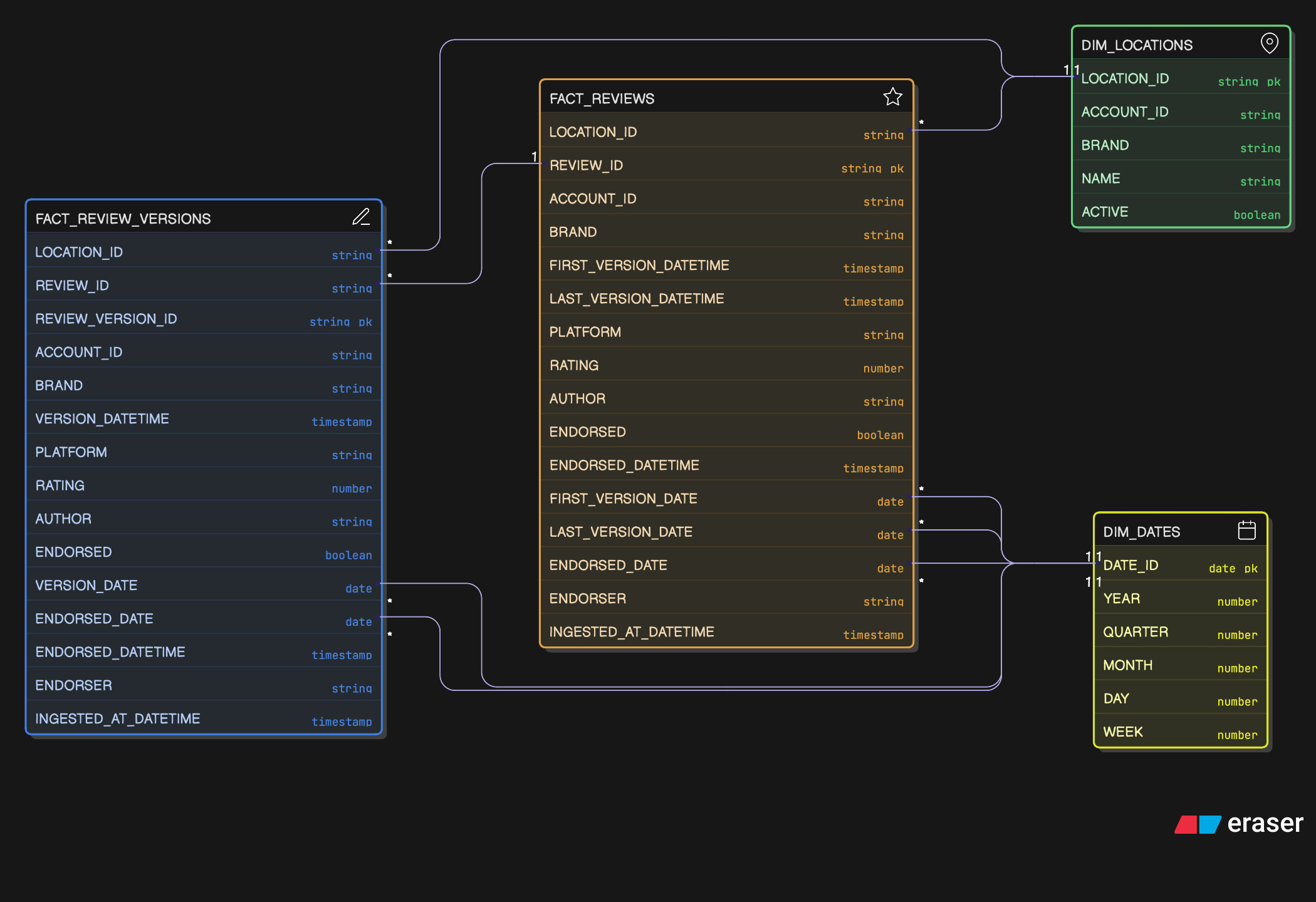
- Reputation (Reviews): Captures and analyzes public reviews and their historical edits. Supports brand health and acquisition reporting.
- Facts:
fact_reviews,fact_review_versions
- Facts:
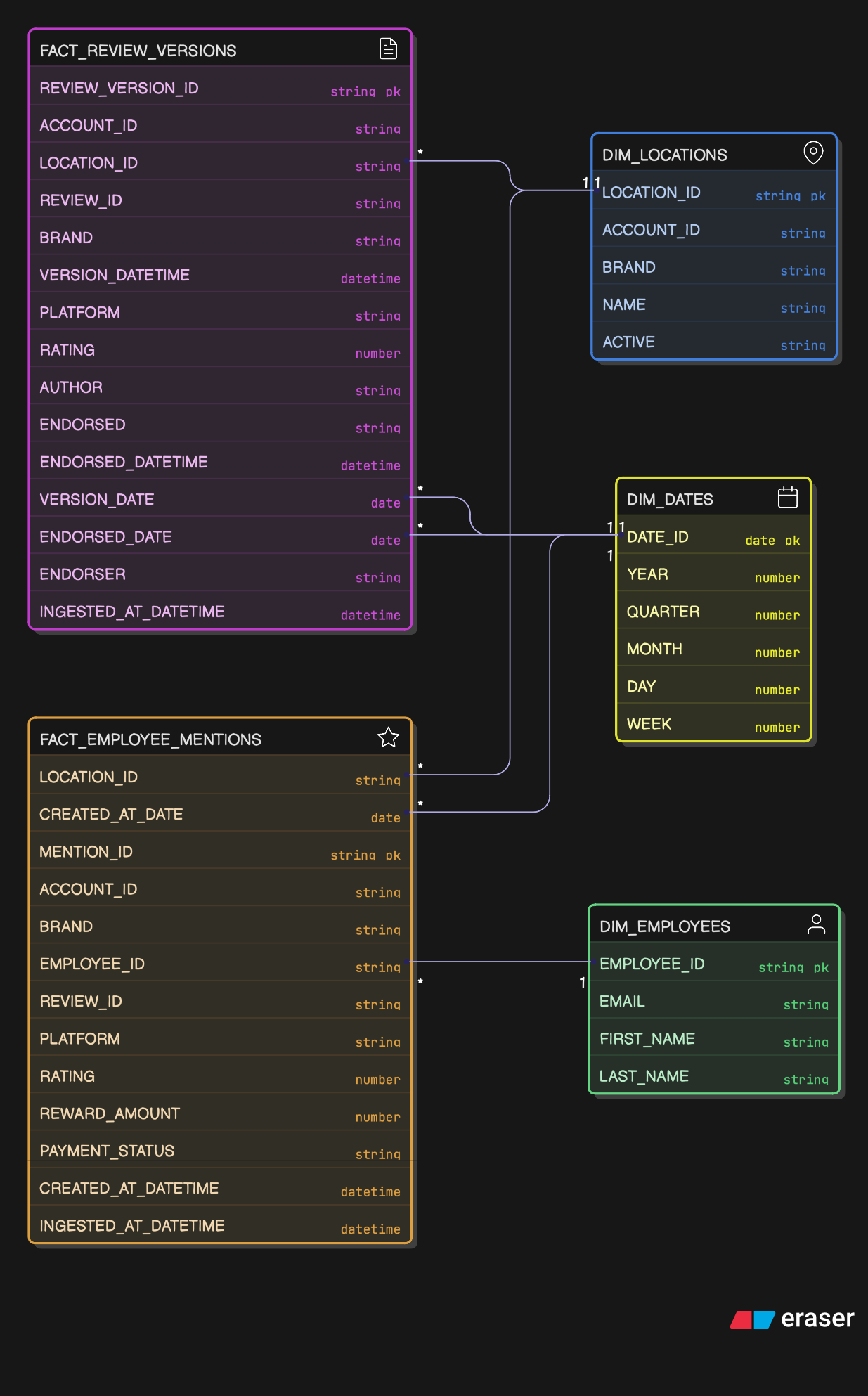
- Employee Recognition (Mentions): Detects employees mentioned in reviews and tracks reward status.
- Fact:
fact_employee_mentions
- Fact:
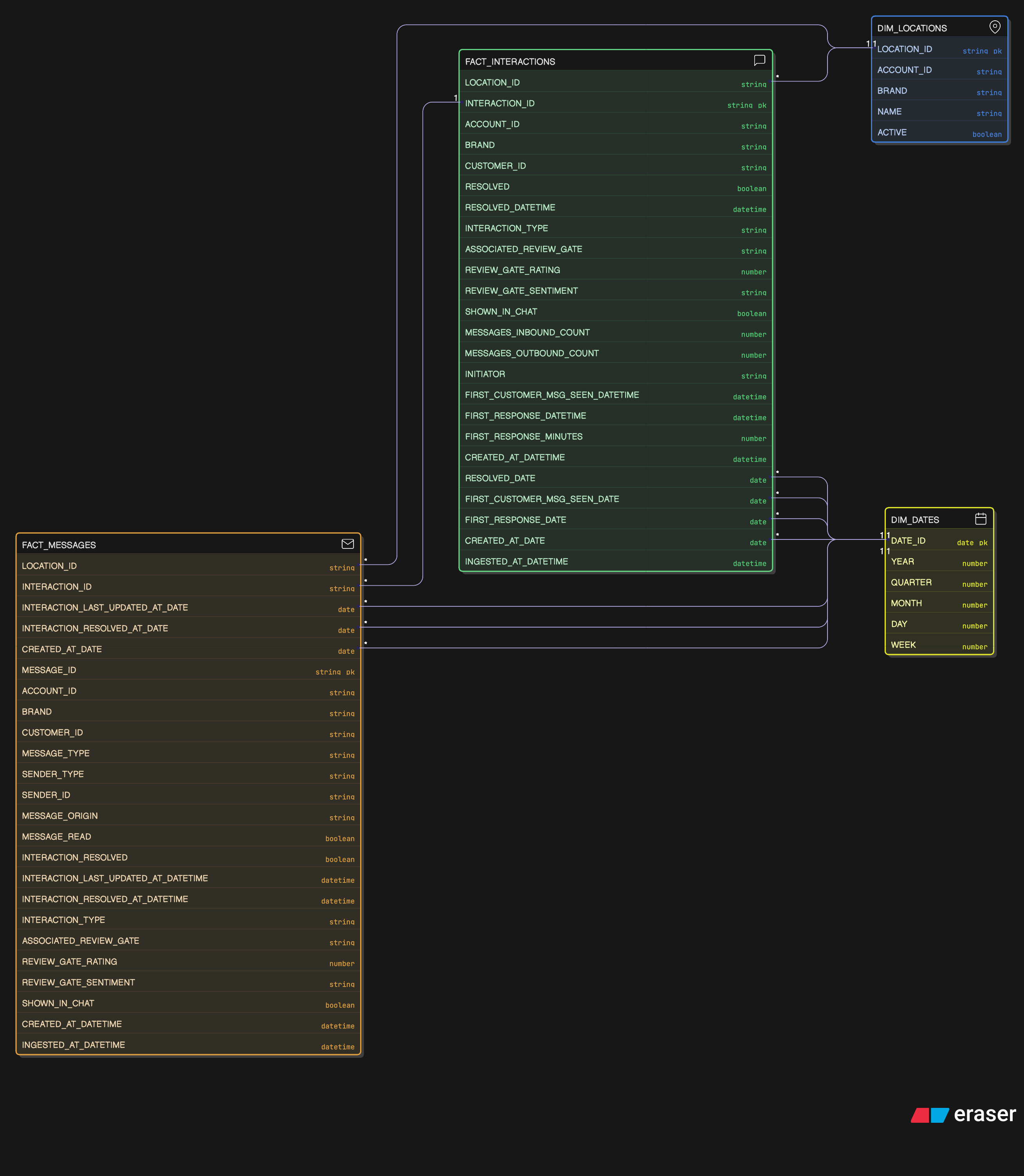
- Messaging & Engagement: Measures guest-business interactions, message mix, and responsiveness.
- Facts:
fact_interactions,fact_messages
- Facts:
- Customer Retention: Quantifies saved revenue and visits attributed to outreach.
- Fact:
fact_customers_saved
- Fact:
- Transactions: Tracks point-of-sale transactions and individual transaction items for revenue and product analysis.
- Facts:
fact_transactions,fact_transaction_items
- Facts:
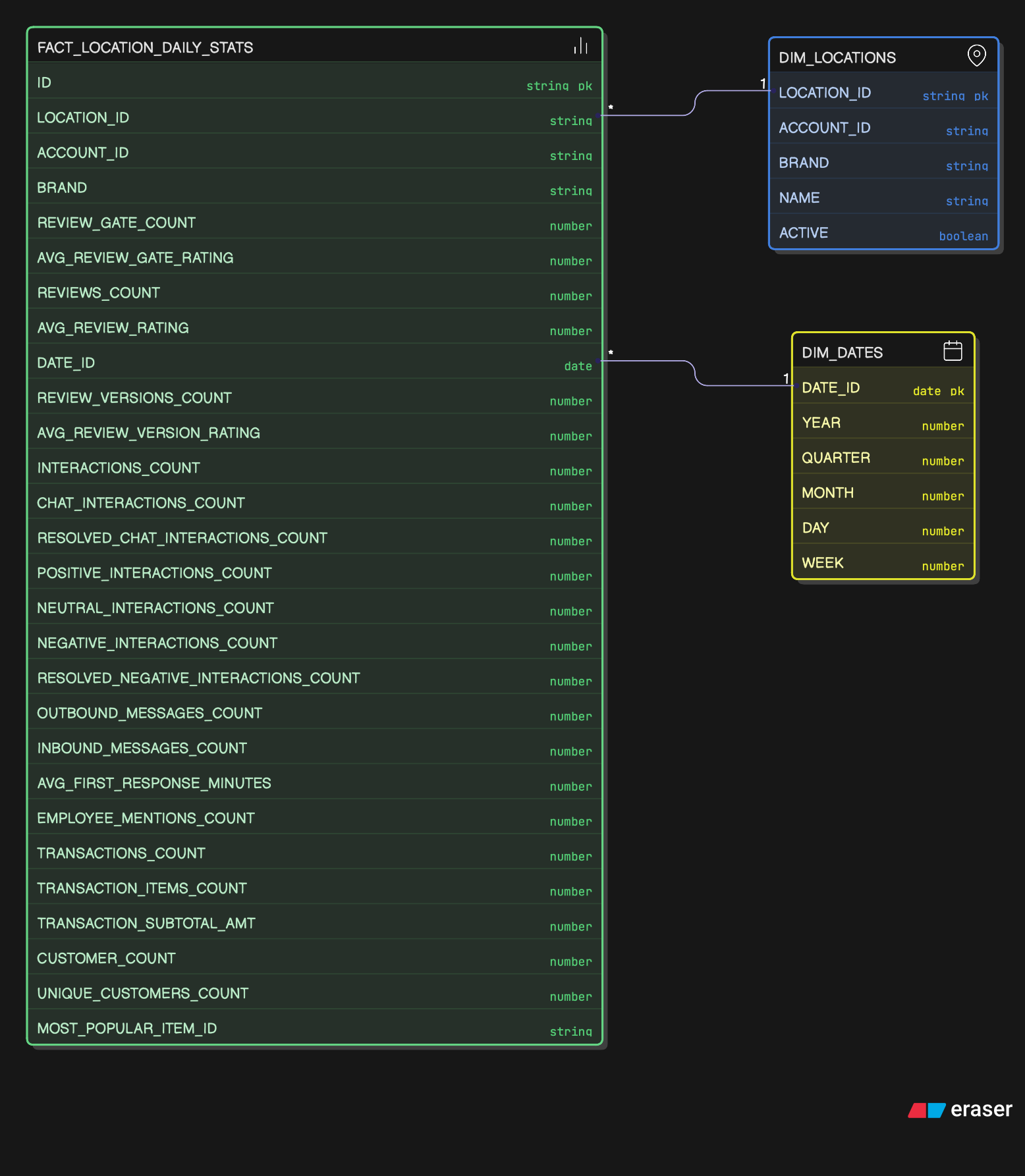
- Location Performance: Provides a daily summary of key metrics for each location, optimized for dashboards.
- Fact:
fact_location_daily_stats
- Fact:
Star Schema Map
| Subject Area | Fact(s) | Grain (One Row Is...) | Conformed Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reputation | fact_reviews | One review (latest state) | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand, Platform |
| Reputation (versions) | fact_review_versions | One observed review version | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand, Platform |
| Employee Recognition | fact_employee_mentions | One employee mention | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, DIM_EMPLOYEES, Account, Brand |
| Messaging & Engagement | fact_interactions | One interaction (engagement) | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand |
fact_messages | One message | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand | |
| Customer Retention | fact_customers_saved | One saved customer profile | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand |
| Transactions | fact_transactions | One transaction | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand |
fact_transaction_items | One transaction line item | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand | |
| Location Daily Performance | fact_location_daily_stats | One (location, date) pair | DIM_DATES, DIM_LOCATIONS, Account, Brand |
Conformed Dimensions: Date, Location, Account, Brand, and Employee are shared across all relevant subject areas.
Subject Area Details
Each section below provides a conceptual diagram and a sample query. For detailed table contracts, see the Facts and Dimensions sections.
Reputation & Reviews
Sample Query: Monthly review volume & rating
SELECT
l.brand,
DATE_TRUNC('month', r.last_version_date) AS month,
COUNT(*) AS reviews_count,
AVG(r.rating) AS avg_rating
FROM fact_reviews r
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE r.last_version_date >= :start_date AND r.last_version_date < :end_date
GROUP BY 1,2
ORDER BY 1,2;
Employee Recognition
Sample Query: Monthly mentions
SELECT
l.brand,
DATE_TRUNC('month', em.created_at_date) AS month,
COUNT(*) AS mentions
FROM fact_employee_mentions em
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE em.created_at_date >= :start_date AND em.created_at_date < :end_date
GROUP BY 1,2,3
ORDER BY 1,2,3;
Messaging & Engagement
Sample Query: Average first response minutes by brand (last 30 days)
SELECT
l.brand,
AVG(i.first_response_minutes) AS avg_first_response_minutes
FROM fact_interactions i
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE i.created_at_date >= DATEADD('day', -30, CURRENT_DATE)
AND i.first_response_minutes IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 1;
Customer Retention

Sample Query: Revenue from customers saved in the past 30 days
SELECT
l.brand,
DATE_TRUNC('month', cs.created_at_datetime) AS period,
SUM(cs.saved_revenue) AS saved_revenue
FROM fact_customers_saved cs
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE cs.created_at_datetime >= DATEADD('day', -30, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP)
GROUP BY 1,2
ORDER BY 1,2;
Transactions
Sample Query: Total transaction revenue and item counts by brand (last 30 days)
SELECT
l.brand,
COUNT(DISTINCT t.transaction_id) AS transactions_count,
SUM(t.transaction_item_count) AS total_items_sold,
SUM(t.transaction_subtotal) AS total_revenue
FROM fact_transactions t
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE t.transaction_datetime >= DATEADD('day', -30, CURRENT_DATE)
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY 1;
Sample Query: Top selling items by location (last 30 days)
SELECT
ti.location_id,
l.name AS location_name,
ti.item_id,
ti.item_product_type,
SUM(ti.item_quantity) AS units_sold,
SUM(ti.item_subtotal) AS revenue
FROM fact_transaction_items ti
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id)
WHERE ti.transaction_datetime >= DATEADD('day', -30, CURRENT_DATE)
GROUP BY 1,2,3,4
ORDER BY 1, revenue DESC;
Location Daily Performance
Sample Query: All-up daily dashboard feed
SELECT
s.date_id,
l.brand,
s.reviews_count,
s.avg_review_rating,
s.interactions_count,
s.positive_interactions_count,
s.inbound_messages_count,
s.outbound_messages_count,
s.avg_first_response_minutes,
s.employee_mentions_count,
s.transactions_count,
s.transaction_items_count,
s.transaction_subtotal_amt,
s.unique_customers_count
FROM fact_location_daily_stats s
JOIN dim_locations l USING (location_id, account_id)
WHERE s.date_id >= :start_date AND s.date_id < :end_date
ORDER BY 1,2;
Table Contracts: Facts
This section details the structure, grain, and change behavior of each fact table.
FACT_REVIEWS (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Latest state of each public review for KPI reporting.
- Grain: One row per review.
- Change Behavior: Mutable snapshot. Late edits upsert the row to reflect the latest state and also append a new record to
fact_review_versions. - Primary Key:
review_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,first_version_datetime,first_version_date,last_version_datetime,last_version_date,platform,rating,author,endorsed,endorsed_datetime,endorsed_date,endorser,ingested_at_datetime. - Notes: Use
last_version_datefor snapshot reporting andfirst_version_dateto track when the review first appeared.
FACT_REVIEW_VERSIONS (Append-Only Event History)
- Purpose: Authoritative history of review edits. Useful for tying back to employee mentions and measuring edit velocity.
- Grain: One row per observed review version.
- Change Behavior: Immutable, append-only table.
- Primary Key:
review_version_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,review_id,version_datetime,version_date,platform,rating,author,endorsed,endorsed_datetime,endorsed_date,endorser,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_EMPLOYEE_MENTIONS (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Latest state of employee mentions within reviews.
- Grain: One row per mention.
- Change Behavior: Mutable snapshot; values such as
employee_idcan be updated (indicating a mention was successfully "matched") - Primary Key:
mention_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,employee_id,review_id,platform,rating,created_at_datetime,created_at_date,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_CUSTOMERS_SAVED (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Tracks revenue saved as a result of using Edge to save dissatisfied customers.
- Grain: One row per saved customer.
- Change Behavior: Mutable snapshot for adjustments to
saved_revenueandsaved_visits. - Primary Key:
customer_id(within the saved event context). - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,saved_revenue,saved_visits,created_at_datetime,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_INTERACTIONS (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Latest state of customer interactions for response SLAs and throughput.
- Grain: One row per interaction.
- Change Behavior: Mutable snapshot; message counts and resolution fields continue to update until the interaction closes.
- Primary Key:
interaction_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,customer_id,interaction_type,associated_review_gate,review_gate_rating,review_gate_sentiment,shown_in_chat,messages_inbound_count,messages_outbound_count,initiator,resolved,resolved_datetime,resolved_date,first_customer_msg_seen_datetime,first_customer_msg_seen_date,first_response_datetime,first_response_date,first_response_minutes,created_at_datetime,created_at_date,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_MESSAGES (Append-Only Event Log)
- Purpose: Captures every individual message sent within an interaction for auditing, coaching, and SLA analytics.
- Grain: One row per message.
- Change Behavior: Mutable snapshot; rich data about the parent interaction is joined onto this row for convenience. As other messages affect the interaction, all other messages in the interaction update with the metadata.
- Primary Key:
message_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,interaction_id,customer_id,message_type,sender_type,sender_id,message_origin,message_read,interaction_resolved,interaction_last_updated_at_datetime,interaction_last_updated_at_date,interaction_resolved_at_datetime,interaction_resolved_at_date,interaction_type,associated_review_gate,review_gate_rating,review_gate_sentiment,shown_in_chat,created_at_datetime,created_at_date,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_TRANSACTIONS (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Point-of-sale transaction data for revenue and customer behavior analysis.
- Grain: One row per transaction.
- Change Behavior: Snapshot table; rows are immutable once posted from POS.
- Primary Key:
transaction_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
location_id,account_id,brand,customer_id,pos_transaction_id,transaction_datetime,transaction_date,pos,transaction_item_count,transaction_subtotal,ingested_at_datetime.
FACT_TRANSACTION_ITEMS (Snapshot)
- Purpose: Individual line items within transactions for product-level analytics.
- Grain: One row per transaction item (denormalized with transaction-level attributes).
- Change Behavior: Snapshot table; line items are immutable once posted.
- Primary Key:
transaction_item_id(surrogate key) - Foreign Key:
transaction_idlinks tofact_transactions. - Attributes:
transaction_id,location_id,account_id,brand,customer_id,pos_transaction_id,transaction_datetime,transaction_date,pos,transaction_item_count,transaction_subtotal,item_id,item_product_type,item_price,item_quantity,item_discount,item_subtotal,ingested_at_datetime. - Note: Transaction-level fields are denormalized into this table for efficient analytics without joins.
FACT_LOCATION_DAILY_STATS (Daily Aggregate)
- Purpose: Pre-aggregated location/day grain feed for dashboards and SLA monitoring.
- Grain: One row per
(location_id, date_id)pair. - Change Behavior: Mutable daily aggregate; counts are recomputed as upstream facts change.
- Primary Key:
id(surrogate key), with natural key(location_id, account_id, date_id). - Attributes:
brand,review_gate_count,avg_review_gate_rating,reviews_count,avg_review_rating,review_versions_count,avg_review_version_rating,interactions_count,chat_interactions_count,resolved_chat_interactions_count,positive_interactions_count,neutral_interactions_count,negative_interactions_count,resolved_negative_interactions_count,outbound_messages_count,inbound_messages_count,avg_first_response_minutes,employee_mentions_count,transactions_count,transaction_items_count,transaction_subtotal_amt,customer_count,unique_customers_count,most_popular_item_id.
Table Contracts: Dimensions
This section details the structure and change behavior of each dimension table.
DIM_DATES
- Purpose: Shared calendar table for all time-based analysis.
- Grain: One row per calendar date.
- Change Behavior: Static (SCD-0). The table is auto-extended monthly.
- Primary Key:
date_id - Key Attributes:
year,quarter,month,day,week,day_name_short,day_name,month_name_short,month_name,is_weekend.
DIM_LOCATIONS
- Purpose: Canonical data for locations and their attributes (brand, region, eligibility program settings, and lifecycle stats).
- Grain: One row per location.
- Change Behavior: SCD-1. Changes to attributes overwrite previous values.
- Primary Key:
location_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
account_id,brand,name,active,industry,internal,us_region_4,us_region_9,state,country,lat,lon,timezone,pos_name,employee_count,first_msg,last_msg,first_review,last_review,review_count_before_edge,review_count_after_edge,review_version_count_after_edge,endorser_program,eligible,payback,threshold,cap,shared_cap,split_payment,payment_program,digital_checks,go_live_datetime,go_live_date,created_at_datetime,created_at_date,ingested_at_datetime.
DIM_EMPLOYEES
- Purpose: Directory for employees referenced in mentions, interactions, and compensation workflows.
- Grain: One row per employee.
- Change Behavior: SCD-1.
- Primary Key:
employee_id(surrogate key) - Attributes:
email,first_name,last_name,ingested_at_datetime.
Performance & Query Patterns
Multi-Fact Query Pattern
The Problem: Joining two or more fact tables directly at the event grain can cause fanout, double-counting, and slow performance.
The Solution: The safe pattern is to aggregate each fact to the same grain first (usually (date_id, location_id)) in separate Common Table Expressions (CTEs), then join the aggregated CTEs on that shared spine.
Click to view the runnable spine-and-CTE template
-- PARAMETERS
-- :start_date :: DATE
-- :end_date :: DATE
WITH
-- 1. Define the spine for your query
spine AS (
SELECT d.date_id, l.location_id
FROM dim_dates d
JOIN dim_locations l ON 1=1
WHERE d.date_id BETWEEN :start_date AND :end_date
),
-- 2. Aggregate each fact to the spine's grain
reviews_daily AS (
SELECT
fr.last_version_date AS date_id,
fr.location_id,
COUNT(*) AS reviews_count,
AVG(fr.rating) AS avg_rating
FROM fact_reviews fr
WHERE fr.last_version_date BETWEEN :start_date AND :end_date
GROUP BY 1,2
),
messages_daily AS (
SELECT
fm.created_at_date AS date_id,
fm.location_id,
SUM(CASE WHEN fm.sender_type = 'CUSTOMER' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS inbound_messages,
SUM(CASE WHEN fm.sender_type = 'LOCATION' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS outbound_messages
FROM fact_messages fm
WHERE fm.created_at_date BETWEEN :start_date AND :end_date
GROUP BY 1,2
),
interactions_daily AS (
SELECT
fi.created_at_date AS date_id,
fi.location_id,
AVG(fi.first_response_minutes) AS avg_first_response_minutes
FROM fact_interactions fi
WHERE fi.created_at_date BETWEEN :start_date AND :end_date
GROUP BY 1,2
),
-- 3. Join the aggregated CTEs on the spine
joined AS (
SELECT
s.date_id,
s.location_id,
rd.reviews_count,
rd.avg_rating,
md.inbound_messages,
md.outbound_messages,
id.avg_first_response_minutes
FROM spine s
LEFT JOIN reviews_daily rd USING (date_id, location_id)
LEFT JOIN messages_daily md USING (date_id, location_id)
LEFT JOIN interactions_daily id USING (date_id, location_id)
)
-- 4. Final projection
SELECT * FROM joined;
Tip: Use the date column exposed by each fact (
last_version_date,created_at_date,transaction_date, etc.) when aligning to theDIM_DATES.
Performance Checklist
- Prune by date first, then by location/brand. This allows the query engine to use partitions effectively.
- Minimize selected columns in your fact CTEs to only what is needed for aggregation.
- Check for fanout by comparing the row count of your final result to the row count of your spine. They should be approximately equal.
- Use the
EXPLAINplan to verify that your query is using partitions and predicates efficiently.
Data Quality & Observability
Known Gaps & Caveats
- Employee Data: Historical data may contain employees without emails. Use
employee_idfor joins only; employees referenced elsewhere will have emails filled out. - Legacy Message Origins: Messages from legacy systems may have
origin = "Unknown". This is not an error for current data but may appear in historical analysis. - Payment Status: The definition of "paid" for employee mentions can be complex due to historical partial payment schemes. Use the latest normalized status fields for consistency.
- Orphaned Employee Mentions: Some historical
PAIDmentions infact_employee_mentionsreferenceemployee_idvalues that no longer exist indim_employees. These records are retained for audit and compliance purposes. When joining todim_employees, use aLEFT JOINand handle NULL employee attributes appropriately.